Quick Product Tips
Blockchains
Learn what exactly a blockchain is, and what kinds of use cases they might facilitate for software products.
A blockchain is a digital ledger or database that stores information in a secure, decentralized manner. Unlike traditional databases, which are typically managed by a single central authority, blockchains are distributed across a network of computers, with each participant having a copy of the same information.
One of the key features of blockchains is that they use cryptography to secure the information they contain. This means that once data is added to the blockchain, it becomes extremely difficult to modify or delete, providing a high level of transparency and immutability.
Blockchains can be used in a variety of scenarios - we share a few of them below.
Supply chain management: Blockchain can be used to create a secure and transparent supply chain system that allows all parties involved to track the movement of goods and verify their authenticity. This can help to prevent counterfeiting and improve supply chain efficiency.
Digital identity management: Blockchain can be used to create a secure and decentralized system for managing digital identities. This would allow individuals to control their own data and provide access to it on a need-to-know basis, while also ensuring that their personal information remains secure.
Smart contracts: Blockchain technology can be used to create self-executing contracts that automatically trigger actions based on pre-defined conditions. This has potential applications in a wide range of industries, including finance, insurance, and real estate.
Voting systems: Blockchain can be used to create secure and transparent voting systems that ensure the integrity of the voting process and protect against fraud.
Decentralized file storage: Blockchain can be used to create decentralized file storage systems that allow users to securely store and share data without relying on a central authority. This can improve data privacy and security, while also reducing the risk of data loss.
As a product manager, it's important to understand the potential benefits and limitations of blockchain technology, as well as the various use cases and industries where it could be applicable. That said, while it might be worth exploring how blockchain could potentially improve the products you're working on or provide new opportunities for innovation, you should remember to focus on addressing the needs of your customers and your business stakeholders.
Remember - product management isn’t about chasing shiny new tech. It’s about creating lasting solutions to unaddressed pain points!
Front End vs. Back End Development
Learn what the difference between front end development and back end development is.
Front end development refers to the creation of the user-facing part of a website or application. This includes the design, layout, and functionality of the user interface that users interact with. On the other hand, back end development refers to the creation of the server-side of a website or application. This includes the databases, servers, and application logic that work behind the scenes to deliver content and functionality to the user.
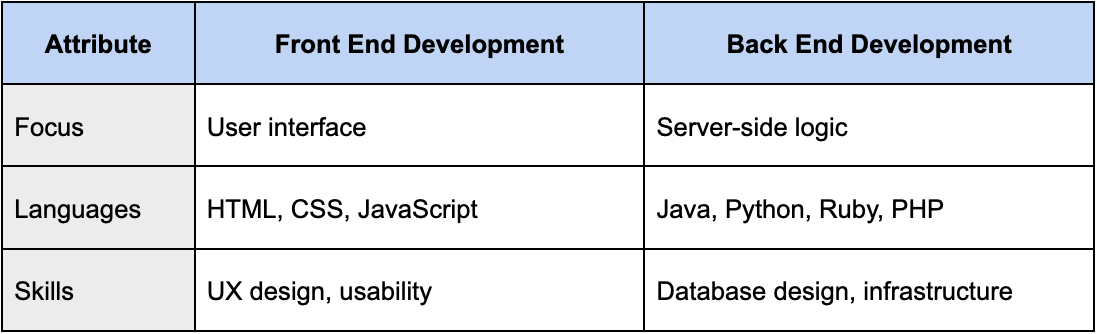
Front end development involves creating the visual elements of a website or application. This includes the layout, colors, typography, and overall design of the interface. Front end developers use HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to create these visual elements and make the website or application interactive. Front end developers need to have a strong understanding of user experience design and web design principles.
Back end development involves creating the server-side of a website or application. This includes creating the databases, servers, and application logic that handle the requests and data from the front end. Back end developers use programming languages such as Java, Python, Ruby, and PHP to create the logic and functionality of the application. They need to have a strong understanding of software development principles and database management.
The following table summarizes some of the key differences between front end development and back end development:
While front end development and back end development are different, they are also interconnected. Front end developers need to work closely with back end developers to ensure that the website or application is properly connected to the necessary servers and databases. This requires good communication and collaboration between the two teams.
In conclusion, front end development and back end development are two different aspects of software development that are both essential to creating a successful website or application. Front end development involves creating the user-facing part of the website or application, while back end development involves creating the server-side of the website or application. Front end developers use HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to create the visual elements and make the website or application interactive, while back end developers use programming languages such as Java, Python, Ruby, and PHP to create the logic and functionality of the application. Both front end development and back end development are important, and they require good communication and collaboration between the two teams to create a successful product.
Data Visualization
Learn what data visualization is and how you can incorporate it into your products.
Data visualization is the graphical representation of data and information. It involves using visual elements, such as charts, graphs, and maps, to present complex data sets in an easy-to-understand format. As a product manager, understanding what data visualization is can help you enhance your products.
One key benefit using data visualization in products is the ability to communicate complex information quickly and effectively. Data visualization can help users to quickly understand trends, patterns, and relationships in data that would be difficult to see in raw data form. This can be especially useful in products that involve large amounts of data, such as analytics dashboards or financial reports.
Yet another benefit of using data visualization in products is the ability to identify new opportunities and areas for improvement. By visualizing data, product managers can identify trends and patterns that may not be immediately apparent in raw data form. This can help product managers to make informed decisions and develop new features or products that address emerging needs or gaps in the market.
Data visualization can also be used to improve the product's user experience. By presenting data in a visually appealing and easy-to-understand format, data visualization can help to engage users and keep them interested in the product. This can be especially important in products that involve complex or technical data, such as healthcare or financial products.
Furthermore, data visualization can also be used to improve collaboration and communication within teams. By visualizing data, teams can quickly identify and address issues or areas of concern, and collaborate more effectively to develop solutions. This can be especially useful in product development teams that involve multiple stakeholders and departments.
Note that integrating data visualization into products requires thoughtful planning. Product managers need to work closely with designers and data analysts to identify the key data points and develop the most effective visualizations. They also need to ensure that the visualizations are properly labeled and easily understandable, and that the data is presented in a way that is both accurate and relevant.
Data visualization is a powerful tool that product managers can use to enhance the products they manage. By communicating complex information quickly and effectively, identifying new opportunities and areas for improvement, improving the user experience, and improving collaboration and communication within teams, data visualization can help organizations stay competitive and provide value to their customers. That said, integrating data visualization into products requires careful planning and execution, and product managers need to collaborate with design and data analysis counterparts to drive success.
Machine Learning
Learn what machine learning is, and how to use it as a product manager.
As a product manager, it is crucial to understand what machine learning (ML) is and how it can be used to enhance the products you manage. Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that involves the use of algorithms and statistical models to enable computers to learn from data and improve their performance on a specific task without being explicitly programmed. In other words, machine learning enables computers to learn from experience and make predictions or take actions based on that experience.
One of the main benefits of using machine learning in products is the ability to automate decision-making processes. Machine learning algorithms can analyze data to identify patterns and make predictions or decisions based on those patterns. This can be especially useful in complex products with large amounts of data, such as financial analysis, fraud detection, and personalized recommendations.
Another benefit of using machine learning in products is the ability to improve the product's user experience. Machine learning algorithms can analyze user behavior and preferences to provide personalized recommendations and suggestions. For example, e-commerce platforms can use machine learning to recommend products to users based on their browsing and purchase history.
Machine learning can also be used to optimize product performance. By analyzing data from sensors or other sources, machine learning algorithms can identify patterns and predict when a product may fail. This can enable proactive maintenance, reducing downtime and improving product reliability.
In addition to these benefits, machine learning can also be used to identify new business opportunities. By analyzing data from multiple sources, machine learning algorithms can identify trends and patterns that may not be immediately apparent. This can enable organizations to develop new products and services that address emerging needs or gaps in the market.
It is important to note that integrating machine learning into products requires careful planning and execution. Product managers need to work closely with data scientists and engineers to identify use cases for machine learning and ensure that the necessary data is available and properly labeled. They also need to ensure that the machine learning algorithms are properly trained and tested to ensure accuracy and reliability.
In conclusion, machine learning is a powerful tool that product managers can use to enhance the products they manage. By automating decision-making processes, improving user experiences, optimizing product performance, and identifying new business opportunities, machine learning can help organizations stay competitive and provide value to their customers. However, integrating machine learning into products requires careful planning and execution, and product managers need to work closely with their data science and engineering teams to ensure success.
Microservices vs. Monoliths
Learn why you might want to transition to a microservices-oriented architecture as a product manager.
In the world of software development, microservices have become an increasingly popular approach for building and deploying applications. Microservices are an architectural style that structures an application as a collection of small, independent services that can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently. This essay aims to explain what microservices are to a product manager and compare and contrast them against a monolith. Additionally, it will discuss why product managers are responsible for helping their engineering teams transition to microservices rather than monoliths.
A monolith is a traditional approach to software development, where the application is built as a single, large codebase. All the functionalities of the application are packaged together and deployed as a single unit. In a monolith, any changes to one part of the codebase can affect other parts, making it difficult to make changes to the application without affecting other parts of the system. Monoliths can be challenging to maintain and scale, and it can be challenging to test new features as they may require the entire application to be rebuilt and redeployed.
Microservices, on the other hand, are an approach to software development that breaks down the application into smaller, independent services. Each service is responsible for a specific functionality and can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently. These services communicate with each other through APIs, and each service can be written in a different programming language or use a different technology stack. Microservices are highly scalable and can be easily tested and deployed. They also provide better fault tolerance and can be more resilient than monoliths.
The following table summarizes some of the key differences between monoliths and microservices:
Microservices offer several advantages over monoliths, including better scalability, fault tolerance, and resilience. They also allow for more flexibility in development, deployment, and testing. However, transitioning from a monolith to microservices requires careful planning and coordination.
Product managers play a crucial role in ensuring a smooth transition from monoliths to microservices. One of their primary responsibilities is to ensure that the product is scalable and can meet the needs of the customers. Monoliths can be challenging to scale as they require a significant amount of resources to scale vertically. On the other hand, microservices can be easily scaled horizontally by adding more instances of a specific service. This allows organizations to scale their services based on demand, ensuring they meet their customers' needs.
Product managers are also responsible for ensuring that the product is reliable and resilient. Monoliths are prone to failure, as any issue in one part of the codebase can bring down the entire application. In contrast, microservices are designed to be resilient, with each service having its own set of resources, and the entire system can continue to function even if one service fails.
Another key responsibility of a product manager is to ensure that the product is developed and deployed quickly. Monoliths can be slow to develop and deploy as any change to the codebase requires rebuilding and redeploying the entire application. In contrast, microservices can be developed and deployed independently, allowing organizations to make changes to specific services without affecting other parts of the system. This can significantly reduce the time it takes to develop and deploy new features and updates.
Transitioning from a monolith to microservices can be challenging, and it requires careful planning and coordination. Product managers play a vital role in helping their engineering teams navigate this transition. They are responsible for identifying the dependencies between different parts of the system and working with their teams to break down the monolith into smaller, independent services. They also need to ensure that the development and deployment processes are optimized for microservices and that the team is adequately trained on this new approach to software development.
In conclusion, microservices offer several advantages over monoliths in software development, including better scalability, fault tolerance, and resilience. Product managers play a crucial role in ensuring a smooth transition from monoliths to microservices by ensuring that the product
Data Lakes
Learn what a data lake is, and how these might impact a product manager’s work.
In today's business world, data is the backbone of many companies. With the explosion of digital technology, organizations are gathering more and more data, which can be used to gain insights, improve operations, and develop new products and services. However, the volume, variety, and velocity of data can be overwhelming, and traditional data management approaches may not be sufficient. This is where data lakes come in.
As a product manager, it is essential to understand what a data lake is and how it can benefit your organization. In simple terms, a data lake is a centralized repository that stores all your organization's structured and unstructured data in its raw form. Unlike a traditional data warehouse, which requires data to be processed and structured before storage, a data lake stores data in its native format, without imposing any restrictions or limitations.
Data lakes can be used to store all types of data, including structured data (such as databases and spreadsheets) and unstructured data (such as emails, social media posts, and video files). This makes it easier for organizations to collect, store, and manage data from multiple sources, without worrying about data format or schema.
One of the key benefits of a data lake is that it allows organizations to store and process large volumes of data at a lower cost compared to traditional data warehousing solutions. With data lakes, organizations can store petabytes of data without having to invest in expensive hardware or software.
Moreover, data lakes are highly scalable, allowing organizations to expand their storage capacity as their data needs grow. This scalability ensures that organizations can store and process data without worrying about storage limitations or bottlenecks.
Another important benefit of data lakes is their flexibility. Unlike traditional data warehouses, which have a fixed schema and require data to be structured before storage, data lakes allow organizations to store data in its native format. This means that organizations can store and process any type of data without worrying about data format or schema. This flexibility allows organizations to experiment with new data sources and data types, without having to worry about data modeling or schema design.
Data lakes also enable organizations to perform advanced analytics on their data. With the ability to store large volumes of data, organizations can perform complex queries and analysis to gain insights and make informed decisions. Moreover, data lakes support a wide range of analytics tools, including machine learning, natural language processing, and predictive analytics, allowing organizations to extract value from their data in new and innovative ways.
However, it is important to note that data lakes require careful planning and management to be effective. Data lakes can quickly become a data swamp if not properly managed, as data can be duplicated or become inconsistent. Organizations need to have a clear strategy for data management, including data quality control, metadata management, and data governance.
In conclusion, data lakes are a powerful tool for managing and processing large volumes of data. As a product manager, it is important to understand what a data lake is and how it can benefit your organization. With the ability to store and process any type of data, data lakes offer flexibility, scalability, and cost savings compared to traditional data warehousing solutions. However, data lakes require careful planning and management to be effective, and organizations need to have a clear strategy for data management to avoid creating a data swamp.
Technical Debt
Learn what technical debt is, and how product managers deal with technical debt effectively.
Technical debt is a term used to describe the amount of time, effort, and resources that a product team needs to invest in order to maintain a product or application over its lifetime. It is typically a result of decisions made in the product development process, such as cutting corners or failing to introduce sufficient quality assurance (QA) measures, and can potentially lead to costly delays, inefficiencies, and a decrease in customer satisfaction. As such, it is essential for product managers to effectively manage technical debt in order to ship and manage successful products.
At its core, technical debt is the result of decisions made by a product team to save time or resources during the product development process. This can include taking shortcuts in the code, using inefficient or outdated methods, or even simply failing to plan for future issues. When a product team takes on technical debt, they are essentially creating a debt that needs to be paid off later— often times with a large amount of additional effort and resources. This can lead to costly delays, inefficiencies, and customer dissatisfaction.
In order to effectively manage technical debt, product managers must first understand the concept and recognize the signs that their product has accumulated technical debt. One of the most obvious signs of technical debt is a decrease in product quality. This could include a decrease in product performance, user experience, or usability. Other signs of technical debt to look out for include increased development time, decreased customer satisfaction, and increased customer support requests.
Once the product team has identified the technical debt in their product, it is important for them to create a strategy to address it. This strategy should include a plan for paying down the debt, such as refactoring the code, introducing QA measures, or fixing bugs. Additionally, product managers should be aware of the potential risks associated with taking on technical debt, such as a decrease in customer satisfaction, increased development time, or a decrease in product quality.
Product teams should also ensure that they have the right tools and resources in place to effectively manage technical debt. This includes having the right development frameworks, testing tools, and debuggers in place. Additionally, product teams should have access to quality assurance specialists who can provide helpful insights into the product and identify areas that may need improvement.
Finally, product managers should implement a process for tracking and managing technical debt. This should include a system for tracking technical debt, such as a workflow system, and a strategy for addressing debt. This strategy should include a plan for paying down the debt and ensuring that the product stays up to date. Additionally, product teams should create an effective communication and collaboration process for addressing technical debt and ensuring that all team members are aware of any changes or updates.
In conclusion, technical debt is a serious issue that can significantly impede the success of a product. As such, it is essential for product managers to effectively manage technical debt in order to ship and manage successful products. This includes understanding the concept of technical debt, identifying signs of technical debt in their product, creating a strategy to address it, and having the right tools and resources in place to manage it. Additionally, product managers should implement a process for tracking and managing technical debt in order to ensure that the product remains up to date and that customer satisfaction is not impacted. By taking the appropriate steps, product managers can ensure that their products remain successful and that technical debt does not become a barrier to success.
User Personas
Learn what user personas are, and how product managers use these tools to build better products.
A user persona is a representation of the target audience for a product or service. It is a composite of the attributes, behaviors, and goals of a typical user that have been determined through research and analysis. Personas are used to create a better understanding of the user and the type of experience they need and expect when engaging with the product or service.
Personas help ensure that the product or service meets the needs of its target audience. By understanding the user’s behaviors, attitudes, and needs, product managers can design and build a product that meets the user’s expectations. Personas can also help identify potential areas for improvement, enabling product managers to make informed product decisions.
User personas are most often developed by conducting interviews, surveys, and other forms of research. Through data analysis and synthesis, product managers are able to generate a profile for each persona, which includes demographic information, background information, behaviors, attitudes, and goals. This information can then be used to build a product that is tailored to the user’s needs and preferences.
For example, a product manager may be considering the development of a new e-commerce website. Through interviews, surveys, and data analysis, the product manager may develop several user personas. These personas may include a “tech-savvy millennial” who prefers a mobile experience, a “working professional” who likes to browse online, and a “thrifty shopper” who wants the best value.
Using this information, the product manager can design and build a website that is tailored to the needs of each persona. The product manager may also use the personas to identify areas for improvement, such as making the website more user-friendly for mobile users, or providing discounts for thrifty shoppers.
User personas are an invaluable tool for product managers when making product decisions. Personas provide insights into the target audience’s behaviors, attitudes, and needs, enabling product managers to design and build products that meet the user’s expectations. Additionally, personas can help identify areas for improvement, enabling product managers to prioritize features and functions when making product decisions. Through research, data analysis, and synthesis, product managers are able to generate a profile for each user persona, enabling them to create products that are tailored to their target audience’s needs and preferences.
Feature Flags
Learn what feature flags are, and how they help product managers ship products more effectively.
A feature flag, also known as a feature toggle or feature switch, is a tool that product managers use to control the display and behavior of certain features in their product. It is a way of controlling the rollout and maintenance of new features so that they can be tested, rolled out gradually, or toggled on and off for certain users or user groups. Feature flags are designed to help product managers to experiment with new features and releases, to test and deploy new features safely and efficiently, and to control access to new features.
Feature flags provide product managers with an efficient and powerful way of managing their product. By using feature flags, product managers can control how and when new features are released. They can deploy new features gradually and with greater control, allowing them to make sure that each feature works properly before rolling them out to all users. Furthermore, feature flags can be used to test new features on a smaller group of users before deploying them to the entire user base. This allows product managers to experiment with new features without risking the stability of the product.
Feature flags can also be used to control access to new features. Product managers can use feature flags to limit access to new features to certain user groups, such as beta testers or customers with special privileges. This allows product managers to test new features on a more controlled group of users before rolling them out to a larger group. It also allows product managers to control who can access certain features, allowing them to protect sensitive data or features from unauthorized access.
In addition to controlling access to new features, feature flags can also be used to disable or enable certain features. This allows product managers to quickly disable or enable features in response to customer feedback or bugs. It also allows product managers to quickly remove features that may be causing problems without having to completely rewrite the code or redeploy the product.
Finally, feature flags are a great way for product managers to keep track of the progress and performance of their product. By using feature flags, product managers can track which features are being used, which ones are not being used, and which ones need to be improved. This allows product managers to quickly identify any potential issues or bugs, as well as areas that could use improvement.
In short, feature flags provide product managers with an efficient and powerful way of managing their product. By using feature flags, product managers can control how and when new features are released, limit access to new features, and quickly disable and enable features. Furthermore, feature flags can help product managers to track the performance and progress of their product. Ultimately, feature flags are an essential tool for any product manager looking to build a better product.
Design Thinking
Learn what design thinking is, and why product teams use design thinking to come up with solutions for customer pains.
Design thinking is an approach to problem solving that has been increasingly adopted by product managers. It is an iterative process that involves a combination of research, brainstorming, and testing in order to create a solution that meets user needs while also considering the constraints and requirements of the project.
At its core, design thinking is a human-centered approach to problem solving that puts the user at the center of the process. Rather than trying to simply solve a problem, it seeks to understand the context of the issue, the motivations of the users, and the constraints of the project. This approach allows product managers to create solutions that are tailored to the specific needs of each project, while also addressing user needs and business goals.
To start, product managers should identify the problem they are trying to solve. Once the problem is identified, it’s important to understand the needs of the users and any constraints that may influence the project. This can be done through a combination of user research, stakeholder interviews, and competitive analysis.
After a problem has been identified and the necessary context and constraints have been established, it is important to brainstorm ideas and potential solutions. This step is often done collaboratively with stakeholders and users, as the input from these groups can help to inform the product design process.
Once ideas have been generated, it is important to test the various solutions that have been proposed. This can take a variety of forms, including user interviews, focus groups, and prototyping. Through testing, product managers can see which ideas are resonating with users, and what changes may need to be made.
Finally, product managers must evaluate the success of their solution. This step typically involves collecting feedback from users, reviewing analytics data, and assessing the product against the original goals of the project. This step is crucial, as it allows product managers to determine which ideas were effective, and which may need to be modified or discarded.
Design thinking is an incredibly powerful tool that can be used by product managers to create effective and innovative solutions. By understanding the needs of the user, and considering the constraints of the project, product managers can create solutions that are tailored to each project and that meet the needs of users. Through user research, brainstorming, and testing, product managers can ensure that the final solution is the most effective and successful possible.
A/B Tests
Learn what A/B testing is, and how product managers use these tests to improve their products.
A/B testing, also known as split testing, is the process of comparing two versions of a product, website, or application to determine which version works better for a given purpose. It is a form of optimization technique used to improve the user experience of a product by allowing product managers to understand customer preferences and make decisions that positively impact customer satisfaction.
A/B testing is an iterative process that begins with the formulation of a hypothesis. A hypothesis is an educated guess or prediction on how a change to the product will affect its performance. Product managers should then create two versions of the product: the original version, which is referred to as the control group, and the modified version, which is referred to as the test group. The two versions are then released to selected users and the results are monitored. By comparing the user behavior on the two versions, product managers are able to determine which version is more successful in achieving the desired goal.
Product managers can use A/B testing to optimize a variety of aspects of their product, from usability and user interface design to content and marketing strategies. For example, if a product manager wants to learn which type of call-to-action button is more effective in increasing conversions, they can run an A/B test by creating two versions of the page, one with a red call-to-action button and one with a green call-to-action button. By releasing the two versions to selected users and monitoring their behavior, the product manager can determine which version of the page is more successful in converting users.
Product managers can also use A/B testing to test how changes to their product affect customer satisfaction and loyalty. For example, if a product manager wants to know whether adding a new feature to the product will increase customer satisfaction, they can run an A/B test by creating two versions of the product: one with the new feature and one without. By releasing the two versions to selected users and measuring their satisfaction levels, the product manager can determine whether the new feature increases customer satisfaction.
Product managers should also use A/B testing to validate their decisions. By testing a hypothesis before making a change to the product, product managers can gain insight into how their users will respond to the change. This helps them make informed decisions and ensure that the changes they are making are in the best interest of their customers.
In summary, A/B testing is a powerful tool that product managers can use to optimize their product and make informed decisions that positively impact customer satisfaction. Product managers should use A/B testing to test new features, identify customer preferences, and validate their decisions. By running A/B tests, product managers can gain insight into how their users respond to changes and make decisions that will improve their product and increase customer satisfaction.
UX for Product Managers
Learn what UX (user experience) is, and why product managers need to consider UX when building products.
UX, or user experience, is the process of creating a product or service that meets customers’ and end users’ needs and expectations. UX is a holistic approach to designing products, services and experiences that meet customers’ needs. It requires a deep understanding of the user's context, motivations, wants and needs. UX designers consider the emotional and physical aspects of the user's experience when designing a product or service.
Product managers need to have a strong grasp of UX principles and basics in order to create successful product designs. Product managers are responsible for the overall direction of a given product. This includes defining the product’s roadmap, roadmap feature sets, and product design. In order to create a successful product, product managers need to have a deep understanding of user experience principles and basics. This understanding will enable them to design products that are both functional and delightful to use.
In order to create a successful product, product managers need to have an understanding of user research. User research is a process that involves interviewing users, observing user behavior, and analyzing data to gain insights into users’ motivations, wants, and needs. User research enables product managers to identify user needs, pain points, and opportunities for improvement. This information can then be used to inform product design decisions. Product managers should also understand usability testing, which is the process of evaluating a product’s usability. Usability testing enables product managers to identify areas for improvement and makes sure that the product is intuitive and easy to use.
In addition to understanding user research and usability testing, product managers need to be familiar with UX design principles. UX design principles are guidelines that help UX designers create products that are both useful and delightful to use. These principles include usability, discoverability, feedback, visual appeal, consistency, and accessibility. Product managers should make sure that the products they design adhere to these principles in order to create a positive user experience.
Finally, product managers need to have an understanding of the different tools and techniques used in the UX design process. These tools and techniques include wireframing, prototyping, user testing, and usability testing. These tools and techniques enable product managers to create products that meet users’ needs and expectations. Product managers should also be familiar with user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) design principles in order to create products with a consistent look and feel across all platforms.
In conclusion, product managers need to have a strong grasp of UX principles and basics in order to create successful product designs. Product managers must understand user research, usability testing, and UX design principles in order to create products that meet users’ needs and expectations. They should also be familiar with the different tools and techniques used in the UX design process, as well as UI and UX design principles. Product managers who understand UX principles and basics will be able to create products that are both functional and delightful to use.
APIs for Product Managers
Learn what an API is, and why product managers need to understand APIs to build winning products.
An API (Application Programming Interface) is a set of tools, protocols, and software that allows two separate applications to interact with each other. It is the bridge between two systems, allowing them to communicate and exchange data in a secure and efficient manner. By using APIs, product managers can unlock valuable data and insights, as well as automate complex processes. Product managers need to understand APIs in order to build successful products.
To illustrate, let's look at a hypothetical scenario. A product manager is in charge of creating a new mobile application that will allow users to order meals from local restaurants. Without an API integration, the product manager would have to manually enter each restaurant's menu items and pricing information into the application. This would be tedious and time-consuming and would also limit the number of restaurants that could be added to the mobile application.
However, with API integration, the product manager can quickly and easily integrate with existing restaurant menus and pricing databases. This allows them to rapidly expand the list of restaurants available on the mobile application without having to manually enter the data. API integration also allows the product manager to easily add new features to the application. For example, they could add a payment integration API, so users can pay for their orders directly from within the application.
API integration is an essential part of building successful products. Not only does it reduce the time and effort required for development, but it also provides valuable data and insights. By integrating with existing data sources, the product manager can gain valuable insights into customer behavior, usage patterns, and preferences. This data can then be used to further refine and improve the product.
APIs also allow for the integration of third-party services and features into the product. This includes features such as marketing automation, analytics, and payment processing. By integrating these third-party services, product managers can quickly and easily add new features and functionality to their products without having to develop them from scratch.
Finally, APIs can also be used to automate complex processes. For example, a product manager could integrate an inventory management API into their product. This would allow them to automatically update the inventory levels of products when orders are placed. This would reduce the amount of manual work required to manage the product and would help to ensure that the product remains up-to-date.
Product managers need to understand APIs in order to build successful products. APIs provide a powerful set of tools and protocols that can be used to quickly and easily integrate with existing data sources, third-party services, and automated processes. This allows product managers to quickly and easily add features and functionality to their products, as well as gain valuable insights into customer behavior and preferences. By understanding and leveraging APIs, product managers can create successful products that stand out from the competition.
Coordination Costs
Learn what coordination costs are, and how product managers can help reduce these costs.
Coordination costs are the costs associated with coordinating work between different departments and individuals in an organization. These costs include the time and effort invested in communication, decision making, and other activities necessary to ensure all the necessary components of a project are met. Coordination costs are often overlooked when calculating the overall cost of a project, yet they are integral to successful project implementation and can have a significant impact on the total cost and timeline.
Product managers should pay close attention to coordination costs, as they can make or break the success of a project. Poor coordination can result in slow or incomplete development, which can lead to increased costs, missed deadlines, and unhappy customers. Coordination costs can also affect the software product's usability, if the product manager fails to consider how different elements of the product need to work together. For example, if the product manager fails to coordinate between the design team and the engineering team, the end result could be a product that looks great but is difficult to use.
Product managers should understand the need for coordination and the costs associated with it. They should be aware of the different resources, tasks, and dependencies involved in a project and take the time to coordinate efforts between teams. This can involve creating a detailed project timeline and breaking down tasks into more manageable chunks, which can help ensure smoother project delivery.
In addition to organizing project tasks, product managers should also pay attention to the cost of communication. The amount of communication needed to coordinate between different teams can quickly add up and become an expensive part of the overall project. Product managers should identify which forms of communication are most effective for different tasks, and use this information to minimize costs.
Product managers should also be aware of how coordination costs can be reduced. For example, they can use tools such as online project management platforms to make collaboration between teams easier and more efficient. They can also use automation tools to reduce manual tasks and make the process of coordination more streamlined.
Overall, coordination costs are an important factor to consider when leading an initiative. Product managers should pay close attention to the costs associated with coordination and take measures to reduce or eliminate them. They should also strive to make processes more efficient, as this can help ensure successful project delivery and reduce costs in the long run. By understanding coordination costs and taking steps to reduce them, product managers can help ensure their projects are completed on time, within budget, and to the highest possible standards.
Objection Handling
Learn what objection handling is, and why it matters for product managers.
Objection handling is a critical component of software product management. At its core, it is the process of acknowledging a customer’s concerns and addressing those concerns in a way that resolves their objections. It is an important skill to have in software product management as it helps ensure that customers are satisfied and that a product meets their needs.
When a customer voices an objection, it can be a sign that there is something lacking in the product’s features or even in the way it is being presented. As software product managers, it is important to take the time to listen to and understand the customer’s objections, and to then address those objections in a way that ultimately leads to a sale.
Objection handling involves more than simply listening to and understanding customer objections. It also involves knowing how to respond to those objections in a way that is beneficial to both the customer and the software product. This requires problem-solving skills that include being able to identify the customer’s needs, to come up with solutions to address those needs, and to understand the importance of customer service.
As software product managers, it is important to keep in mind that objection handling is not just about resolving customer objections; it is also about building relationships. Objection handling is a great opportunity to demonstrate the value of the product, to provide customer service, and to show that the software product manager is truly invested in the customer’s experience. Objection handling is also an opportunity to build trust and long-term relationships, which is essential in software product management.
In conclusion, objection handling is a critical component of software product management. It is the process of acknowledging a customer’s concerns and responding to those concerns in a way that resolves their objections and leads to a sale. Objection handling requires problem-solving skills, the ability to identify customer needs and come up with solutions to address those needs, and a commitment to providing excellent customer service. It is also an opportunity to build trust and long-term relationships with customers, which is essential for success in software product management.
Value Propositions
Learn what a value proposition is and how product managers establish value propositions.
A value proposition is a statement that outlines a company’s offering and how it brings value to the customer. In the context of software products, a value proposition is the promise of a product to provide a benefit that will make customers choose it over the competition. The value proposition should be clear, concise, and easy to understand. It should be tailored to the target audience and should include the features and benefits of the product.
Product managers play a crucial role in creating and refining value propositions for software products. Product managers are responsible for understanding customer needs, developing the value proposition, and ensuring that the value proposition is communicated to potential customers. Product managers must have a deep understanding of their product’s features and benefits and be able to use this knowledge to create an effective value proposition.
The first step in creating a value proposition is to identify the customer’s needs. Product managers must research the target market and understand their needs, wants, and pain points. This can be done through market research, customer interviews, surveys, and focus groups. Once the customer’s needs are understood, the product manager can then create a value proposition that meets these needs.
Next, product managers must identify the unique features and benefits of the product. This should include both the tangible and intangible benefits that the product provides. Examples of tangible benefits are cost savings, faster speed, and improved performance. Intangible benefits are things such as satisfaction from using the product and a sense of belonging to a community. Product managers must also be able to articulate these features and benefits in a way that resonates with customers.
Finally, product managers must ensure that the value proposition is communicated to potential customers. This can be done through various channels such as website copy, blog posts, case studies, and customer testimonials. Product managers should also use customer feedback to refine the value proposition and ensure that it meets customer needs.
In conclusion, product managers are responsible for creating and refining value propositions for software products. They must have a deep understanding of their product’s features and benefits and be able to articulate these in a way that resonates with potential customers. Product managers must also ensure that the value proposition is communicated to potential customers through various channels. By doing this, product managers can create value propositions that will help their products stand out from the competition.
Sprints for Product Managers
Learn what a sprint is in the context of product management.
Software development is a complex process that requires a great deal of planning and strategy. One of the most important tools for software development is the sprint. A sprint is a period of time when designers and engineers work together to achieve a specific goal. Product managers should understand what a sprint is in order to effectively plan out their own work and that of their team. This essay will explain what a sprint is and how it is used in software development.
What is a Sprint?
A sprint, in software development, is a period of time in which a team of designers and engineers work together to achieve a specific goal. The length of the sprint is typically two to four weeks, though it may be shorter or longer depending on the needs of the project. The sprint is often used in Agile software development, which focuses on small, incremental improvements to the software.
During the sprint, the team works together to plan out their tasks and determine the best way to complete them. Each day of the sprint starts with a stand-up meeting, where the team reviews the progress that was made the previous day and plans out the tasks for the day. This is an important part of the sprint, as it ensures that everyone is on the same page and that tasks are completed in a timely manner.
The sprint also includes regular check-ins between the team and the product manager. These check-ins allow the product manager to track the progress of the sprint and provide feedback to the team. The product manager can also provide guidance and assistance as needed.
Benefits of a Sprint
The sprint is beneficial for both the team and the product manager. By focusing on a specific goal, the team can work together in an efficient and effective manner. This allows them to complete tasks quickly and accurately. Additionally, the stand-up meetings serve as a way for the team to stay on track and ensure that tasks are completed in a timely manner.
For the product manager, the sprint provides them with an easy way to track the progress of the team. The regular check-ins allow the product manager to provide feedback and guidance to the team, as well as catch potential problems before they become an issue. This helps the product manager ensure that the software is developed in a timely and accurate manner.
Conclusion
The sprint is an important tool for software development. It allows a team of designers and engineers to work together in an efficient and effective manner. The sprint also allows the product manager to track the progress of the team and provide feedback and guidance as needed. By understanding what a sprint is and how it is used, product managers can better plan out their own work and that of their team.
Blended Metrics
Learn what a blended metric is, and why product managers sometimes use these to make product decisions.
A blended metric, or composite metric, is an aggregated measure of an overall value or performance. This metric can be derived from the analysis of multiple individual metrics to provide an overall understanding of a product’s health or performance. Product managers may turn to blended metrics to gain a more comprehensive understanding of their product’s success or failure, rather than relying on only one single metric.
The purpose of a blended metric is to offer a more holistic approach to evaluating a product’s performance, rather than relying solely on a single metric. This can be especially valuable when multiple metrics are used to measure different aspects of a product. By combining these individual metrics into a single blended metric, the product manager can gain a better understanding of the big picture.
For example, a product manager may want to evaluate the success of a new feature launch. To do this, they might track multiple metrics such as the number of downloads, the number of active users, the average daily users, and the average session time (AST). By combining these metrics into a blended metric, the product manager can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the feature’s success or failure. A blended metric could be calculated to show the percentage of users who are actively using the feature, or the average session time per user. This blended metric would give the product manager a better understanding of the overall engagement with the feature.
Blended metrics can also be used to measure customer loyalty or satisfaction. For example, a product manager might track customer satisfaction metrics such as the number of reviews and ratings, the Net Promoter Score, customer complaints, and customer support requests. By combining these metrics into a single blended metric, the product manager can gain a better understanding of the overall customer satisfaction with their product.
Finally, blended metrics can be used to evaluate the overall performance of a product. For example, a product manager might track metrics such as the number of downloads, revenue, user activity, customer satisfaction, and engagement. By combining these metrics into a single blended metric, the product manager can gain a better understanding of the overall health of the product.
Overall, blended metrics can offer a comprehensive understanding of product performance and success. By combining multiple individual metrics into a single blended metric, product managers can gain a better understanding of the big picture. This can help them make more informed and data-driven decisions when it comes to product development and management.
User Interviews
Learn what user interviews are, and how product managers use them on the job.
User interviews are a crucial step in the product development process. They provide product managers with valuable insight into how users interact with a product, what needs and wants they have, and what potential problems and issues may exist. User interviews are a powerful tool for product managers to gain an understanding of their target audience, which is essential for making informed product decisions.
The goal of user interviews is to identify the needs, motivations, and goals of users, and then use this information to make informed product decisions. User interviews are conducted with a specific target audience and involve asking both general and specific questions in order to gain a comprehensive understanding of the user’s experience with the product. User interviews involve listening and actively engaging with users to obtain feedback and insight into their experiences.
Product managers should use user interviews to gain an understanding of users’ motivations and needs, as well as to identify potential problems. By having an understanding of users’ motivations and needs, product managers can better design products that are tailored to user needs and expectations. Additionally, user interviews can help to identify potential problems, allowing product managers to anticipate and address these issues before they become major issues.
In addition to understanding users’ needs and motivations, user interviews can also provide product managers with valuable insight into the user experience. User experience encompasses all aspects of a user’s interaction with a product, from the first time they use it to the last. By understanding the user experience, product managers can better design products that are both intuitive and efficient. Furthermore, user interviews can help to identify any potential issues with the user experience, allowing product managers to address them before they become major issues.
Another important use of user interviews is to identify potential opportunities for product improvement. By engaging with users and understanding their needs and wants, product managers can identify potential areas for product improvement. For example, a user may mention that they would like a feature that is not currently included in the product. This user feedback can then be used to initiate product changes and improvements.
In conclusion, user interviews are an invaluable tool for product managers. They provide a comprehensive understanding of users’ needs and wants, as well as potential problems and opportunities for product improvement. By taking the time to conduct user interviews, product managers can be sure that their product decisions are informed and well-thought-out.
Critical Path Method
Learn what the critical path method is and why it can help you out as a product manager.
The Critical Path Method (CPM) is a technique that helps product managers to break down complex tasks into smaller, more manageable components. CPM involves analyzing all the individual tasks that comprise an initiative and organizing them into logical sequences. It also helps product managers to identify the relationships between tasks and which tasks can’t start until others have been completed. The Critical Path Method is an important tool for product managers when it comes to planning, scheduling, and managing initiatives.
Product managers use the Critical Path Method to develop a timeline for an initiative by identifying the tasks that need to be completed and the dependencies between the tasks. The Critical Path Method identifies the tasks that must be completed in order for the initiative to be successful and the tasks that can be delayed or skipped, if necessary. It also helps product managers to determine how much time and resources need to be allocated to each task. This helps ensure that the initiative is completed on time and within budget.
The Critical Path Method works by calculating the duration of each task, and the earliest and latest timing for task completion. Once the total initiative duration and timings have been determined, the product manager can begin to allocate resources to the tasks. This helps to ensure that the right resources are available at the right time in order to complete the initiative on time and within budget.
One of the key benefits of using the Critical Path Method is that it allows product managers to identify and address potential problems before they become serious roadblocks. By analyzing the task relationships, product managers can identify any potential problems, such as tasks that require additional resources or tasks that are dependent upon each other for completion. This allows product managers to adjust the schedule and allocate additional resources, if necessary, in order to keep the initiative on track.
Another benefit of the Critical Path Method is that it allows product managers to better manage risks. By analyzing the tasks and the dependencies between them, product managers can identify potential risks and develop strategies to mitigate them. This helps to ensure that the initiative is completed successfully and that any potential risks are addressed in a timely manner.
In summary, the Critical Path Method is an important tool for product managers. It helps them to plan, schedule, and manage initiatives in a more efficient and effective way. It also helps them to identify and address potential problems and risks before they become serious roadblocks. Product managers should be familiar with the Critical Path Method and how to use it in order to ensure that their initiatives are completed on time and within budget.